
After reading Part 1 of “Plant Trees to Transform Your Landscape”, you’ve located the best spot where a tree will shade the house from brutal summer sun. Recommendations and practices presented here are based on climate and soil in the eastern part of the United States, where I live and garden, but the basic principles apply everywhere.
If your main objectives are shade, attracting wildlife, and less grass to mow, include masses of shrubs and perennials in the landscape plan as well. This article concentrates on planting trees, the dominant features in the landscape.
Native Plants vs. the Non-Natives
The choices offered in garden centers can be narrowed down to native species and non-native, or exotic, species. Within each of those groups are the original species and the cultivars (cultivated varieties). Developed by plant breeders, cultivars exhibit more ornamental or desirable—or just different—characteristics than the species.

‘Red Filigree Lace’, a delicate cultivar of Japanese maple.
Non-native plants originated in a different country or perhaps only a few hundred miles away. If the plant doesn’t occur naturally in your geographic region, it’s non-native, although some gardeners restrict use of the term to plants evolving in another country.
There are many beautiful plants, exotic to our shores, which we’ve enjoyed in our gardens. Japanese snowbell (Styrax japonica), Stewartia pseudocamellia, and the dizzying assortment of Japanese maples (Acer palmatum) are just too hard to pass up. You can compromise, if you wish, by including both natives and exotics.
To most garden center visitors, none of this matters. We buy plants that solve problems and look pretty in our yards. But, to explain the relevance of native species, I’d like to expand the subject.
The Benefits of Native Species
First, native plants require less pampering to get them established.
Species that evolved locally can tolerate fluctuations in weather patterns. Temperature extremes, rainfall, humidity, soil types, altitude, wind patterns, and local fauna shaped today’s ecosystems.
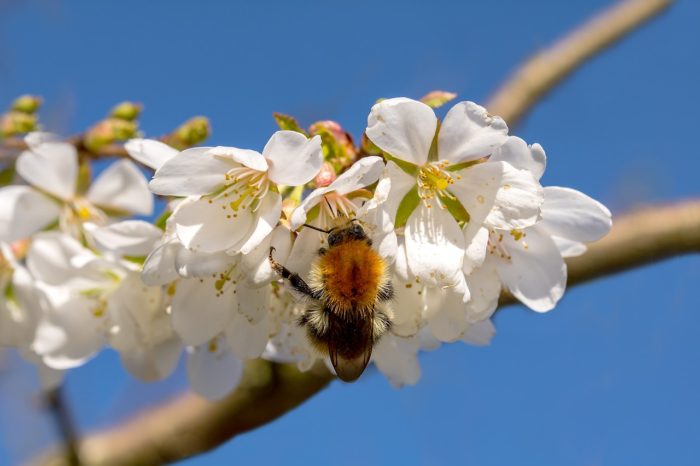
Second, gardeners concerned about local pollinators choose plants that foster bees, butterflies, and other animals that pollinate farm crops and wild vegetation.
Every third bite of food we consume is attributable to pollinators. But, you might make the case that since most crops are alien to this country, it shouldn’t matter whether we use native or non-native trees. But we need to consider what larval insects consume, and that’s foliage and other plant parts. Thousands of species—not just bees—pollinate our farms, orchards, fields, and forests.
Egg-laying female moths and butterflies, beetles, and other insects are very selective and seek the natives they evolved with to supply sustenance for the following generation.
Incidentally, honey bees are not native to this part of the world. They will, however, forage from plants grown here, many of which are related to the plants they evolved with.
Making a Case For Single Flowers
-

-
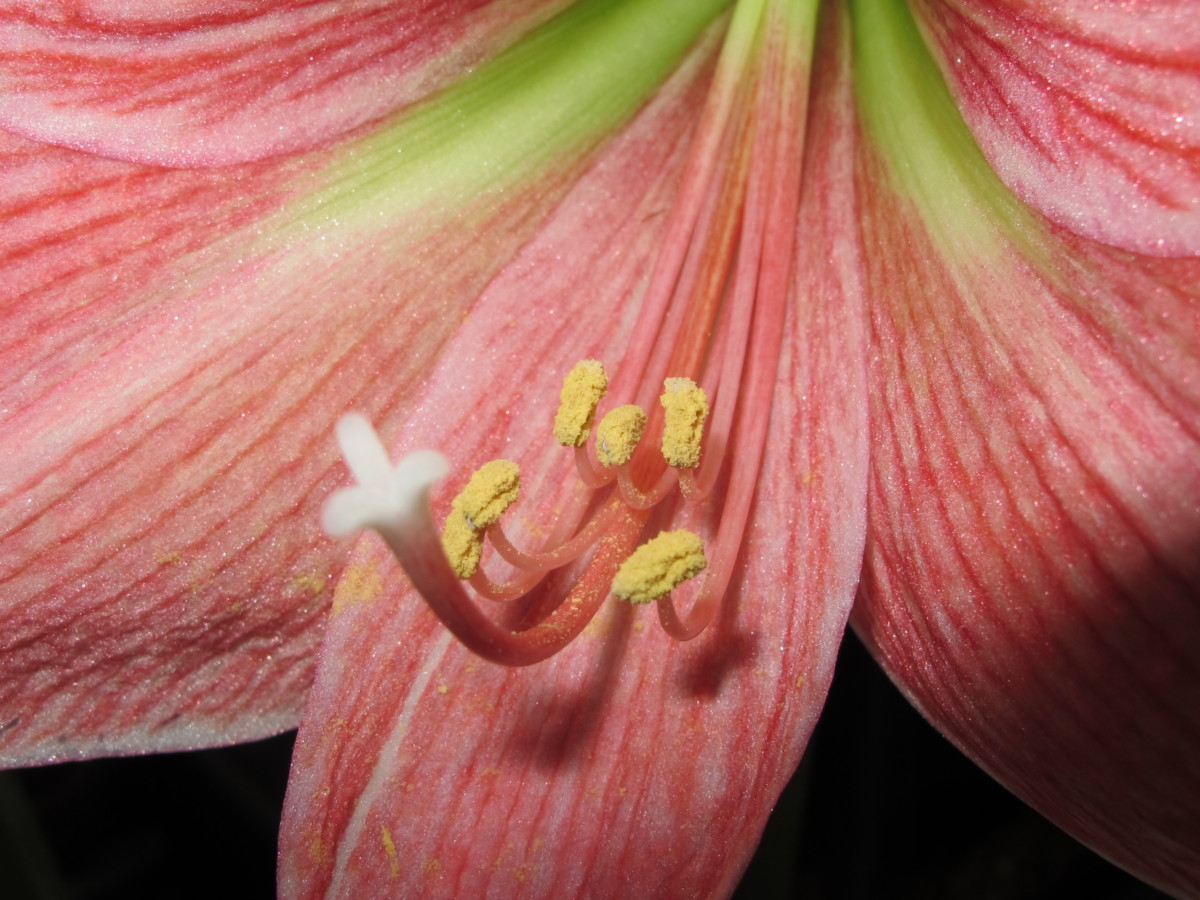
Amaryllis with yellow pollen and white stigma.
-

-
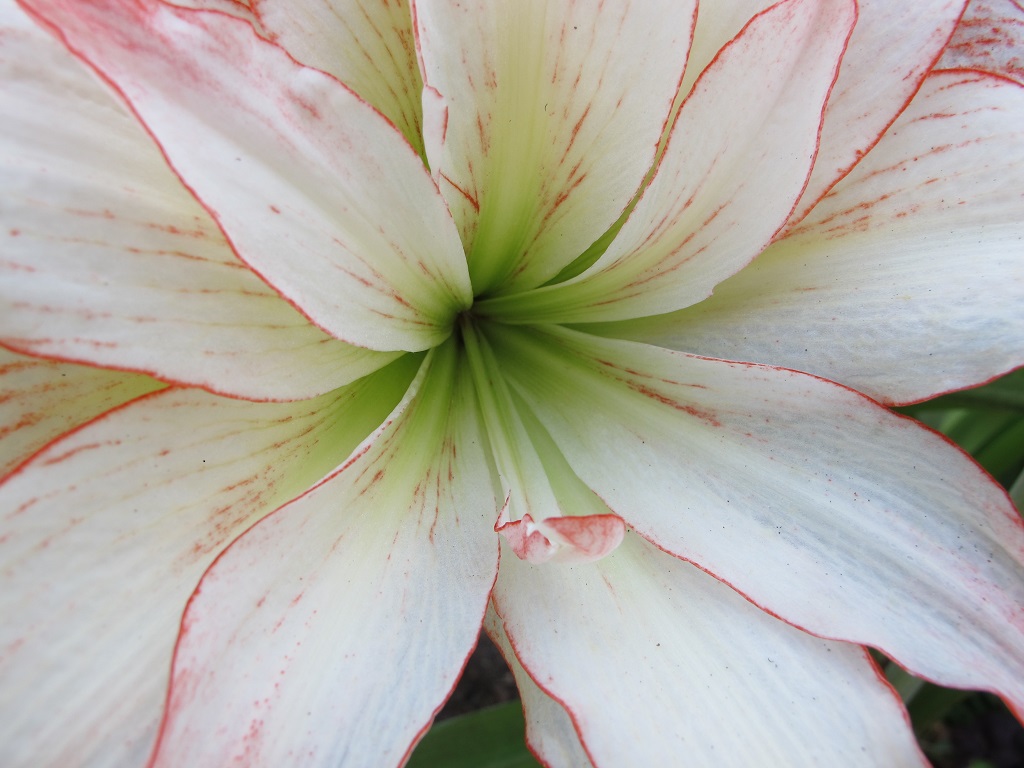
Double amaryllis with no anthers or stigma.
Flowers attract pollinators, which reap the harvest of nectar and pollen. But many double- and triple-petaled flowers have lost their nectaries, stigmas, and/or pollen-tipped stamens. Photos above clearly illustrate the loss of reproductive parts in a double amaryllis cultivar. If these hybridized doubles and triples have lost the ability to reproduce sexually, they can’t make seeds. They must instead be propagated asexually, or vegetatively, by cuttings, division, grafts, or tissue culture.
The anthers, supported by filaments, bear the pollen; the male portion of the flower, collectively, is called the stamen. Female parts comprise the stigma, supported by the style, and the ovary, with its ovules, deeper within the receptacle; the female portion is called the pistil.
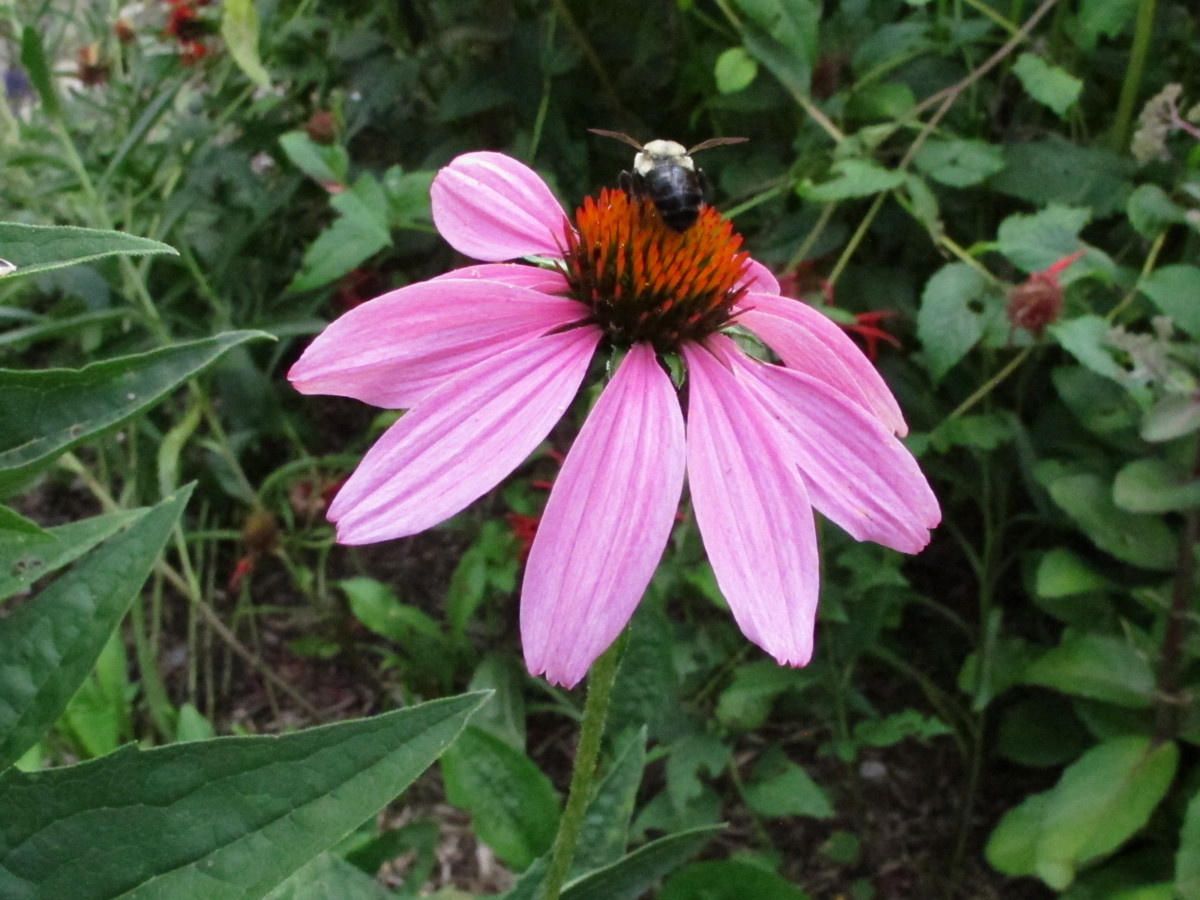
Not all dense flower heads are pollinator wastelands, though. Species in the Asteraceae family, for example, have flowers that normally look full. This family includes all the composites, such as aster, coneflower, daisy, dandelion, rudbeckia, and sunflower. Their dense inflorescences are composed of small florets arranged in a head, called a capitulum. But the original species also have the necessary reproductive parts. The composites are one of the most successful groups of plants and are found on every continent except Antarctica.
At a local garden center last year, I watched bumble bees that were quick to land on thickly-petaled hybrid red coneflowers (Echinacea). They were equally hasty in their departure! The bees stayed on the red flowers for a fraction of a second, while they lingered on the less frilly flowers of other cultivars, mining several florets in each flower for their treasure.
Pollinators waste precious energy visiting barren double-flowered hybrids. True, not all doubles lack nectar and pollen. For the pollinators’ sake, though, select more species or varieties with simple flowers. Natural selection favors plants that set seed, of course, which is why most native plants have simpler flowers.
Photos below show examples of single-flowering cultivars. If you see a boss of stamens and pistils in the flowers, those plants can probably supply pollen and nectar to the pollinators. This is a fine point, granted, but one that is critically important to populations of pollinators, given the preponderance of double-flowering hybrids at garden centers.
-

-
Bumble bee on perennial aster.
-

-
Pollinator on fruit tree.
-

-
Purple coneflower (Echinacea) with bumble bee.
Third, planting a multitude of native species helps secure the future of threatened or endangered insects and animals.
In many regions, songbird populations have declined by half due to human intervention. Some have disappeared entirely. Trees and shrubs that provide shelter, nesting sites, berries or seeds, and which host insects, can help bring back the birds. Abundant biodiversity is a valid protection against the domino collapse of interdependent species.
Civilization has claimed much of the insects’ natural environments, so each of us can play a small part in rebuilding habitats. Annual butterfly counts show drastic declines. Monarch butterflies, in particular, now have less territory available in Mexico, a major overwintering site, than in the past, when they migrated by the millions.
Maintaining brush piles for overwintering insects and animals will help repopulate your landscape early in the season. Hauling those materials off to the recycling center, however, is sure death for the insects tucked inside. Fewer insects = fewer birds and other animals.
Fourth, incorporating native plants into the landscape helps keep the entire food chain intact.

A green anole basking in morning sun.
Insects feeding on plants become food for frogs, lizards, birds, and mammals. They, in turn, become food for snakes, hawks, foxes, and other predators. In many ecosystems, insects native to the region are the foundation on which the entire food chain is based.
A rich diversity of plant material supports an enormous number of insect and animal species. Left undisturbed, populations find a balance among themselves. On the other hand, life in monoculture, such as a lawn, is sparse. Unfortunately, countless urban and suburban neighborhoods have become dead zones with all their natural vegetation bulldozed to the ground.
As we spray, mow, burn, or build in natural environments, species will continue their rapid decline. Certainly, we need places to live and work, but we can also “give back” by planting for wildlife on our own properties, instead of continually killing it off.
Check with your state’s native plant society, native plant finders, BeeCity USA, and the local agricultural extension service for information. In addition to these sources, find a knowledgeable salesperson at the garden center for practical advice and sources of plant material. Garden shows and farmers’ markets might feature vendors specializing in native plants as this branch of horticulture grows.
Native Species and Nativars

Red fall color in a native white oak tree.
Plant breeders have brought to the marketplace many cultivars of our native species. These nativars might have purple or red foliage instead of green, or double flowers instead of single. Perhaps they mature at a shorter height than the original species, making them a better fit for small properties.
Garden centers often stock varieties of native species, although those selling native plants might also stock the original species. By a comfortable margin, though, most of the trees and shrubs in U.S. garden centers are cultivars of non-native species. Many originated in Asia, a treasure trove of tempting horticultural novelties.
Red Leaves and Wildlife

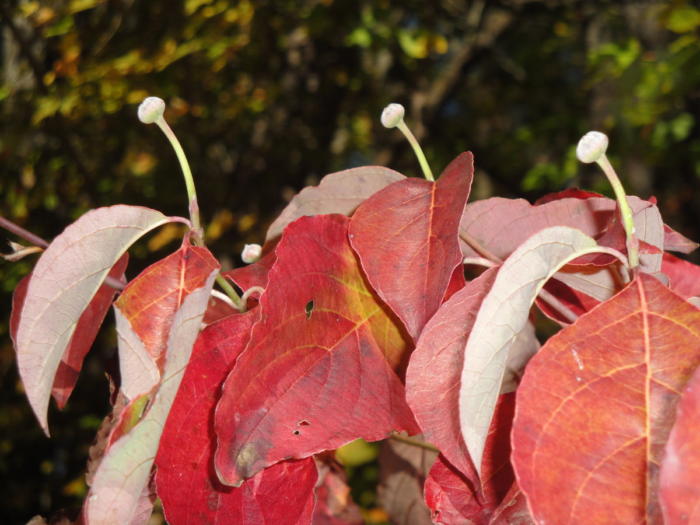
Red fall color and flower buds on native flowering dogwood.
Many trees develop red or burgundy fall foliage. Species native to the eastern U.S. with red fall foliage include sourwood (Oxydendrum arboreum), flowering dogwood (Cornus florida), black gum (Nyssa sylvatica), red maple (Acer rubrum), sugar maple (Acer saccharum), red oaks (Quercus rubra, Q. coccinea), and white oak (Quercus alba).
Beautiful fall color lures camera-toting visitors each year to the mountains, to New England, and to the Blue Ridge Parkway. The U.S. National Park Service provides an interactive map which tracks the progression of fall color.
Red- or purple-leaved cultivars sporting this color all summer are in high demand at garden centers. But if the point of planting trees and shrubs is partially to benefit insects and animals, we want to be sure the plants we choose will attract them. Each plant species has a particular menu of chemical compounds in their tissues that either attract or repel wildlife. Organisms evolved a tolerance for these compounds…or they didn’t!
Purple and red leaves often repel insects due to their high levels of anthocyanins, the red pigments in the foliage. So, that defeats the purpose, doesn’t it? Not necessarily; these trees might have had green leaves that hosted insects before leaves turned red. Or insects simply tolerate the red pigments.
Oak trees support huge numbers of insects, birds, and mammals at various times during the year. This one genus, Quercus, hosts hundreds of species of moths and butterflies throughout its range, although these species often turn red in autumn.
Before planting a cultivar that stays red all season, find out if insects, such as mature caterpillars, will eat the leaves. This indicates that it could host insects for their entire life cycle. If all the larvae are tiny, however, when some larger individuals are expected, most might have crawled off to greener pastures. Or they could have died off.
Planting some red-leaved trees is okay if you have other trees available for the insects. Ultimately, though, it’s your property, so you can plant what you please.
If bees spend time working a flower and don’t fly off immediately after landing, that plant could be a good choice. Similarly, holes in the leaves indicate that the plant can host insects. Resources at the local university’s entomology department or botanical garden might have information that could help you choose plants that support wildlife.
The Untold Story
(This section added 10/6/21.)
I’ve been packing the past couple of weeks, preparing to move to a rural location in northern North Carolina. I took a break from the work and sat on the deck, listening to the birds and insects.
One of those sounds was the hum of an approaching ruby-throated hummingbird, the only species summering in this area. Four feet away, and less than 4″ long, this tiny bird landed on a twig of the potted native dogwood tree, sitting right next to me.
He then hovered near the flower buds (photo, above, with last year’s fall color), and I could see his tongue working the buds, one after another. These buds are tightly closed, yet he found something worth gathering, despite the presence of other flowers nearby.
Within a minute, another hummingbird arrived for the same reason, apparently. The two tiny birds fought for feeding rights, and the second one flew away after some impressive aerial maneuvering among the twigs. The first hummingbird continued searching for hidden sustenance held inside those buds. I’ve never seen this behavior.
My point is this: there’s much about the natural world that remains unobserved—a mystery to us—perhaps lending more credibility to the importance of using native plants in our gardens.
Deciduous Trees For the Eastern U.S.
Here’s a partial list of native and non-native trees that support wildlife. Large deciduous shrubs can substitute for trees in smaller spaces. Many other species might suit your purpose, so visit a few nurseries to see what’s available.
Most trees are sold in large plastic nursery pots, although you might also see freshly dug trees with their roots wrapped in burlap (“b&b”, or balled and burlapped).
- American hop hornbeam (Ostrya)
- basswood (Tilia)
- birch (Betula)
- black gum (Nyssa)
- Carolina silverbell (Halesia)
- chaste tree (Vitex)
- cherry and plum (Prunus)
- crabapple (Malus)
- crape myrtle (Lagerstroemia)
- dogwood (Cornus)
- franklin tree (Franklinia)
- fringe tree (Chionanthus)
- hornbeam (Carpinus)
- magnolia (Magnolia)
- maple (Acer)
- oak (Quercus)
- poplar, cottonwood (Populus)
- redbud (Cercis)
- serviceberry (Amelanchier)
- sourwood (Oxydendrum)
- willow (Salix)
- winterberry (Ilex verticillata)
- witch hazel (Hamamelis)

Native red maple can have yellow, orange, or red fall color.
Most of the trees listed above have small- or medium-sized species or varieties. Compare suitability of native and non-native species within the genus. The familiar weeping willow, for example, is non-native and can pose problems when planted near underground pipes. But smaller native willows behave better and host a large number of moths and butterflies.
Research disease resistance, flowers for pollinators, fruits for animals, sun or shade preferences, and soil types. Consider planting species that drop excessive amounts of fruit, acorns, or seedpods farther from the house and paved surfaces.
Also look into the tree’s habit of growth. A specimen with horizontal branches softens the strong vertical lines of a house. Pay close attention to utility poles and wires. Don’t plant trees near them that the utility company will butcher in future years.
Trees with invasive surface roots should be reserved for areas far from structures, pipes, and vegetable gardens. Find out from your town how close to the street or the property line you’re permitted to plant trees. Don’t forget to call 8-1-1 to locate underground utilities before digging.
Chionanthus, the fringe tree (photo, below), is a beautiful bloomer for gardens. This multi-stem plant has 2 species commonly available (C. virginicus, C. retusus), one native and the other from Asia. Male plants have larger flowers, but females set deep blue fruits for birds. The plants, however, are rarely sexed at the nursery.

Fringe tree.
The Hollies
Gardeners have used hollies in gardens for centuries. We can choose among deciduous and evergreen species.
 The hollies (Ilex spp.) are another genus of primarily dioecious (Latin for “two houses”) plants that fruit on female plants. They ordinarily require a male plant, or pollenizer, to set fruit, although holly pollenizers (the males) themselves do not set fruit. Modern breeding techniques have yielded several cultivars that can make berries without pollination.
The hollies (Ilex spp.) are another genus of primarily dioecious (Latin for “two houses”) plants that fruit on female plants. They ordinarily require a male plant, or pollenizer, to set fruit, although holly pollenizers (the males) themselves do not set fruit. Modern breeding techniques have yielded several cultivars that can make berries without pollination.
Ask your nursery salesperson for specifics regarding the need for pollenizers and how close they should be planted to female hollies. Choose the male hollies carefully; they must be closely related to the female holly and bloom at the same time. Incidentally, holly flowers are often nicely fragrant, and the bees love them! Just don’t shear them off after the buds have formed. Pruning should be minimal if you want flowers and fruits. And bees.
The Curious Case of Crape Myrtle

The Imperial moth.
Lagerstroemia indica is an extremely popular landscape tree or shrub in USDA zones 7-9. Crape myrtle, from China and Korea, was first introduced to the southeastern U.S. over 200 years ago. Adapting readily to our hot, humid summers and sometimes drought, it blooms for months despite the adversity.
What makes this non-native plant peculiar is a native moth’s preference for its leaves even when offered a multitude of its local favorites. Last year, I raised caterpillars of the huge Imperial moth. They went for the crape myrtle every time, ignoring all the others. Unless female moths instinctively target this species to host their young, the caterpillars will not likely eat these trees to the bone any time soon.
Several songbirds, including American goldfinches and juncos, feed on the seedpods.
Evergreens
You might prefer an evergreen specimen instead of a tree that drops its leaves in autumn. Look into arborvitae, chamaecyparis, hemlock, certain holly species, juniper, pine, rhododendron, spruce, and yew. Consider the shade evergreens will cast in winter, and whether sunlight might be blocked from entering windows or melting ice on the driveway.
Although not all evergreens are native to this part of the country, they make suitable nesting places and provide shelter in inclement weather. A dense border of evergreens can block fierce winter wind for a considerable distance downwind.
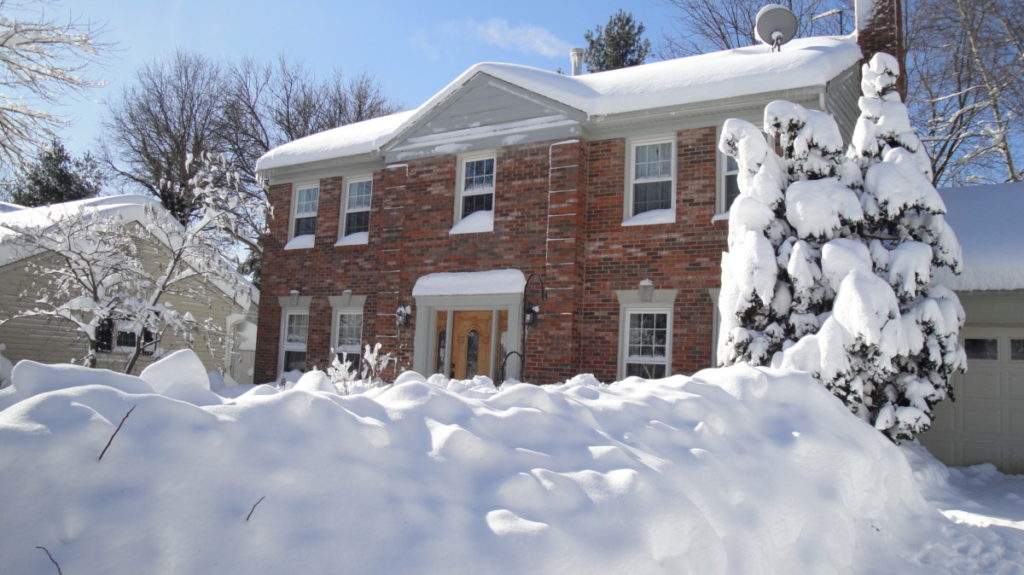
Soon after moving into the Maryland house in the 1980’s, I planted a chamaecyparis with deep green whorled foliage. Although it was supposed to get only 6′ tall according to the nursery, it grew to about 20′, when it was cut down by the people who bought the house from me. I left it in the front yard because birds raised a few families among its evergreen branches every year. And it looked gorgeous in the snow.

Chamaecyparis on the right, after 2010 blizzard. Sourwood on the left.
Good Looks
If you’re landscaping purely for aesthetics, plant a tree with characteristics that appeal to you. It’s your property, after all. Besides, all trees provide cover and nesting opportunities, even if they’re passed up by caterpillars.
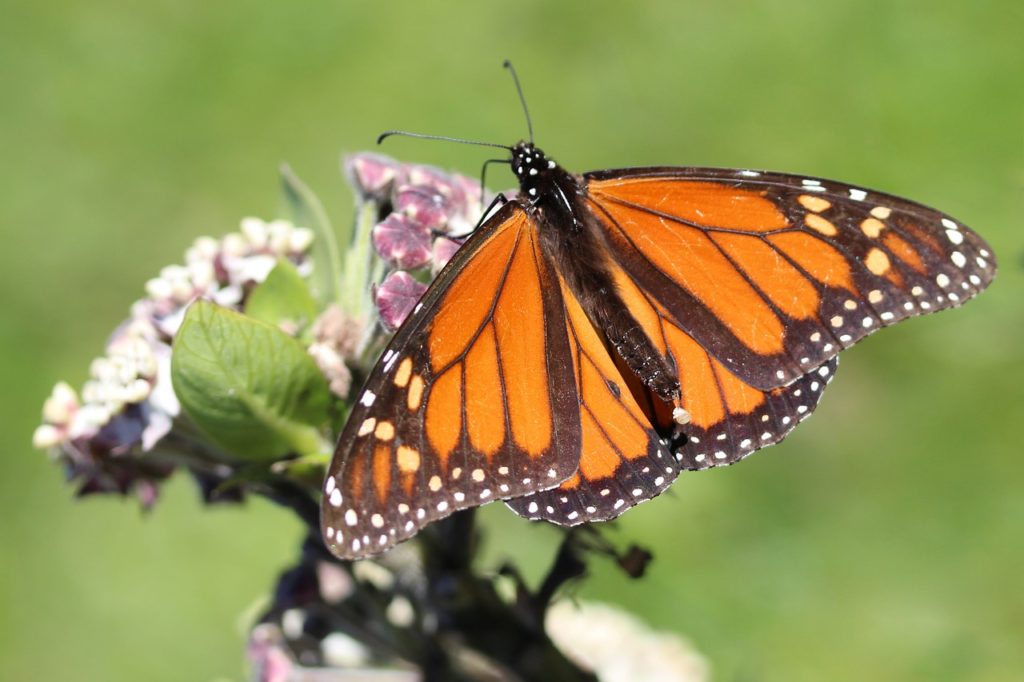
Perhaps elsewhere you could grow perennials that offer food to wildlife. Planting a bed of milkweeds among the shrubs, for example, will help the monarch butterflies (photo, below).
While you might not consider insects important in your landscape, and, in fact, have invested considerable time and expense eradicating them, they are primary links in the food chain. A healthy landscape hosts a complex assortment of insects and animals. And with the rate at which natural habitats are losing out to development, it’s no wonder we see fewer ladybugs, butterflies, and songbirds in our neighborhoods.
Creating welcoming landscapes provides resting places for migrating birds. But they need natural corridors all along their path in order to find food and perching opportunities. We can help by planting at least part of our property with them in mind—every one of us! Provide food, water, and trees to rest in, and you might catch a glimpse of a bird you’ve never seen before.
I urge you to adopt a new attitude toward welcoming wildlife. You don’t need 10 acres to make a difference. A well-planted fraction of an acre will encourage many kinds of insects and animals to reside there. If you let them eat your plants and the sprayer hasn’t been used once this year, well done!

Monarch butterfly on milkweed.
Before Planting Trees
Let’s imagine a 2-story house and an appropriately proportional medium-sized tree. Your landscape plan calls for locating this tree off the southwest corner in the front of the house.
To prevent branches from rubbing against the siding in the future, you’ll want to plant the tree far enough from the house. Divide the mature spread of the tree by 2. Because plants tend to grow larger than the dimensions printed on the label, add a few feet to the measurement. So, a tree with a mature spread of 25-30′ should be planted 15′ or more from the corner.
While that little tree might look lonely out there, it will grow. Maybe that’s the extent of your garden project this fall. Or perhaps you’d like to develop a full garden on that side of the house with an underplanting of shrubs, perennials, and ground covers.
Walking a pathway through the garden to the side yard will feel like a walk through a park. This is a good solution where space is limited between your house and the neighbor’s. Consider your neighbor, though, and don’t plant too close to the property line. Perhaps the two of you could create an appealing garden that fills the space between both houses.
But first, it’s soil prep…please turn to page 2…
Headings:
Page 1: Are You Ready To Plant Trees?, Native Plants vs. the Non-Natives (The Benefits of Native Species, Native Species and Nativars, Red Leaves and Wildlife, The Untold Story), Deciduous Trees For the Eastern U.S. (The Hollies, The Curious Case of Crape Myrtle, Evergreens), Good Looks, and Before Planting Trees
Page 2: Soil Preparation For Trees (Slope, Outline the Bed, Heavy Clay, “How Deep?”, Adding Amendments, Organic Matter, and Time To Plant Trees (Trees In Pots, B&B Trees, Backfill, Edge, Mulch, And Water)
Return to the top
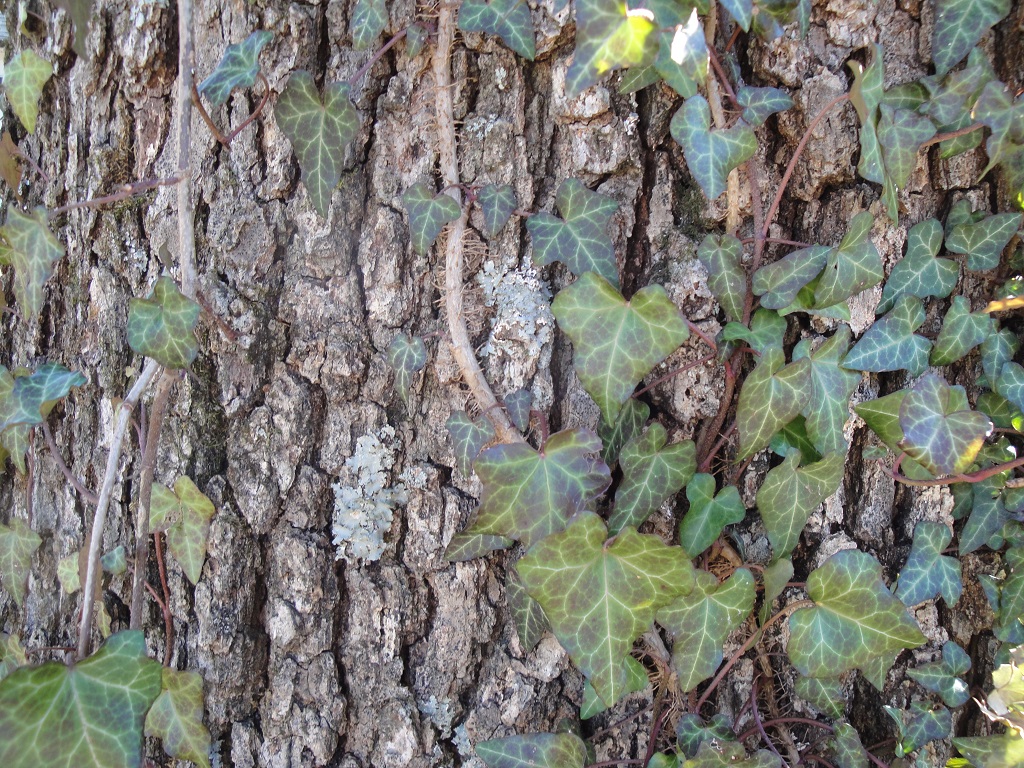




 First, English ivy is a woody vine, so its stems will grow in girth just as a tree branch does. As they wrap around the tree trunk or the limbs and thicken over the years, the ivy stems will constrict tree growth, killing limbs and possibly the tree.
First, English ivy is a woody vine, so its stems will grow in girth just as a tree branch does. As they wrap around the tree trunk or the limbs and thicken over the years, the ivy stems will constrict tree growth, killing limbs and possibly the tree.















 The hollies (Ilex spp.) are another genus of primarily dioecious (Latin for “two houses”) plants that fruit on female plants. They ordinarily require a male plant, or pollenizer, to set fruit, although holly pollenizers (the males) themselves do not set fruit. Modern breeding techniques have yielded several cultivars that can make berries without pollination.
The hollies (Ilex spp.) are another genus of primarily dioecious (Latin for “two houses”) plants that fruit on female plants. They ordinarily require a male plant, or pollenizer, to set fruit, although holly pollenizers (the males) themselves do not set fruit. Modern breeding techniques have yielded several cultivars that can make berries without pollination.




 Find garden space that gets full sun for the best yields. Strawberries start growing before the end of winter, when the sun is still low in the sky. Take this into consideration when locating your garden. In partial sun, foliage and fruits might be plagued by diseases that ruin the crop.
Find garden space that gets full sun for the best yields. Strawberries start growing before the end of winter, when the sun is still low in the sky. Take this into consideration when locating your garden. In partial sun, foliage and fruits might be plagued by diseases that ruin the crop.































 In 1977, the Consumer Product Safety Commission banned the use of lead paint in residential properties. If you live near an industrial region, a busy highway, or where lead paint might be a concern, I strongly advise testing for lead before you prepare the soil. Local zoning authorities should have records on past property use. For more information, contact the National Lead Information Center at 800 424-5323.
In 1977, the Consumer Product Safety Commission banned the use of lead paint in residential properties. If you live near an industrial region, a busy highway, or where lead paint might be a concern, I strongly advise testing for lead before you prepare the soil. Local zoning authorities should have records on past property use. For more information, contact the National Lead Information Center at 800 424-5323.